Fe Cation Charge
Nickel(IV) Ni4+ lead(IV) Pb4+ Roman numeral notation indicates charge of ion when element commonly forms more than one ion. For example, iron(II) has a 2+ charge; iron(III) a 3+ charge. As there is only one iron ion, its charge must be 2+. It is an iron (II) ion, as opposed to iron (III) ion (which has a charge of 3+). A few elements, all metals, can form more than one possible charge. For example, iron (Fe) atoms can form 2+ cations or 3+ cations. Cobalt (Co) is another element that can form more than one possible charged ion (2+ and 3+), while lead (Pb) can form 2+ or 4+ cations. Cations (multiple oxidation state) Name (Roman numeral gives the positive charge!) Polyatomic Ions To: memorize: Name Fe: 3+ iron(III) NH 4 + ammonium Fe: 2+ iron(II) NO 2-nitrite Cu: 2+ copper(II) NO 3-nitrate Cu+ copper(I) SO 3 2-sulfite Cr: 3+ chromium(III) SO 4: 2-sulfate: Ni2+ nickel(II) OH-hydroxide: Pb4+ lead(IV) PO 4 3-phosphate Pb.
What is the charge on the iron cations in iron(II) chloride and iron (III) chloride, respectively?
1 Answer
The Roman numerals after the name of the iron cation indicates the charge on the iron cation.
Explanation:
When naming ionic compounds which contain metal ions capable of forming more than one kind of cation, the Roman numeral after the metal's name indicates the charge.
Periodic Table With Ion Charges
Therefore, the iron cation in iron(II) chloride has a charge of
This video provides some additional examples of how to use Roman numerals when naming compounds.
In the image below, a solution of iron(III) chloride is on the left side and a solution of iron(II) chloride is on the right side.
Phosphorus Charge
Related questions
Department of Chemistry and Physics |
| Answers |
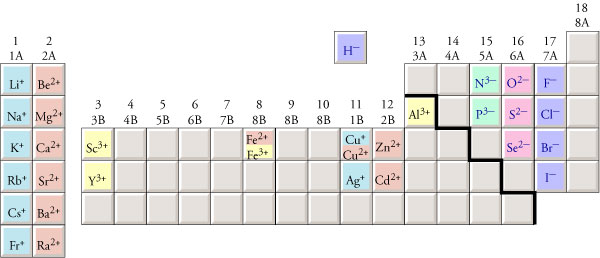
Fe Cation Charge Definition
| Name | Formula | Name | Formula |
| zinc | Zn+2 | chromium(II) | Cr+2 |
| mercury(II) | Hg+2 | hydronium | H3O+ |
| ferric | Fe+3 | manganese(II) | Mn+2 |
| hydrogen | H+ | strontium | Sr+2 |
| silver | Ag+ | nitronium | NO2+ |
| barium | Ba+2 | stannic | Sn+4 |
| magnesium | Mg+2 | mercuric | Hg+2 |
| chromic | Cr+3 | iron(III) | Fe+3 |
| copper(I) | Cu+ | calcium | Ca+2 |
| sodium | Na+ | lead(II) | Pb+2 |
| calcium | Ca+2 | manganese(III) | Mn+3 |
| tin(II) | Sn+2 | ammonium | NH4+ |
| nitronium | NO2+ | potassium | K+ |
| manganous | Mn+2 | hydronium | H3O+ |
| chromium(III) | Cr+3 | tin(IV) | Sn+4 |
| mercury(I) | Hg2+2 | ferrous | Fe+2 |
| strontium | Sr+2 | copper(II) | Cu+2 |
| copper(I) | Cu+ | chromous | Cr+2 |
| manganic | Mn+3 | lithium | Li+ |
| magnesium | Mg+2 | mercury(I) | Hg2+2 |
| stannous | Sn+2 | manganese(III) | Mn+3 |
| cuprous | Cu+ | iron(II) | Fe+2 |
| iron(III) | Fe+3 | barium | Ba+2 |
| hydrogen | H+ | chromium(II) | Cr+2 |
| potassium | K+ | iron(II) | Fe+2 |
| lead(II) | Pb+2 | mercury(II) | Hg+2 |
| lithium | Li+ | cupric | Cu+2 |
| manganese(II) | Mn+2 | mercurous | Hg2+2 |
| ammonium | NH4+ | tin(IV) | Sn+4 |
| sodium | Na+ | chromium(III) | Cr+3 |
| silver | Ag+ | zinc | Zn+2 |
| tin(II) | Sn+2 | copper(II) | Cu+2 |
Fe Cation Charge Calculator
Give either the name or formula (with the correct charge) for each of the anions:Sulfur Ion Charge
| Name | Formula | Name | Formula |
| hypobromite | OBr- | phosphate | PO43- |
| fluoride | F- | formate | HCOO- |
| acetate | CH3COO- | carbonate | CO32- |
| bromide | Br- | nitrite | NO2- |
| bromate | BrO3- | amide | NH2- |
| formate | HCOO- | sulfate | SO42- |
| dichromate | Cr2O72- | hydride | H- |
| chloride | Cl- | iodate | IO3- |
| oxalate | C2O42- | nitrate | NO3- |
| chlorate | ClO3- | hydrogen carbonate | HCO3- |
| arsenate | AsO43- | chromate | CrO42- |
| sulfite | SO32- | phosphate | PO43- |
| peroxide | O22- | thiocyanate | SCN- |
| arsenite | AsO33- | permanganate | MnO4- |
| cyanate | OCN- | hydrogen sulfate | HSO4- |
| cyanide | CN- | chromate | CrO42- |
| hydride | H- | dihydrogen phosphate | H2PO4- |
| nitride | N3- | chloride | Cl- |
| sulfate | SO42- | nitrate | NO3- |
| hydrogen sulfate | HSO4- | arsenite | AsO33- |
| thiosulfate | S2O32- | fluoride | F- |
| sulfite | SO32- | bromide | Br- |
| hydroxide | OH- | iodide | I- |
| thiocyanate | SCN- | iodate | IO3- |
| permanganate | MnO4- | sulfide | S2- |
| chlorite | ClO2- | oxide | O2- |
| hypochlorite | OCl- | hypobromite | OBr- |
| nitride | N3- | hydrogen phosphate | HPO42- |
| carbonate | CO32- | chlorite | ClO2- |
| hydrogen carbonate or bicarbonate | HCO3- | dichromate | Cr2O72- |
| oxalate | C2O42- | bromate | BrO3- |
| nitrite | NO2- | sulfide | S2- |
| acetate | CH3COO- | perchlorate | ClO4- |
| hydrogen phosphate | HPO42- | arsenate | AsO43- |
| oxide | O2- | iodide | I- |
| cyanide | CN- | amide | NH2- |
| cyanate | OCN- | peroxide | O22- |
| chlorate | ClO3- | dihydrogen phosphate | H2PO4- |
| thiosulfate | S2O32- | hypochlorite | OCl- |
| hydroxide | OH- | perchlorate | ClO4- |